36.9 Celsius to Fahrenheit: Understanding Temperature Conversion and Its Importance
Introduction
Temperature is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, influencing our environment, health, and overall well-being. We encounter temperature measurements regularly, whether it’s checking the weather forecast, cooking, or monitoring our body’s health. One of the most commonly encountered temperatures is 36.9°C, often noted in medical contexts when measuring body temperature. But what does 36.9°C mean in Fahrenheit? How do we convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, and why is it important to understand temperature conversions? In this article, we will explore these questions, delving into the conversion process, the history behind temperature scales, and their practical applications.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
Before we dive into the conversion, it is essential to understand the difference between the Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature scales, as they are the most widely used systems of temperature measurement globally.
Celsius Scale (°C)
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, was developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. The scale is based on two fixed points: the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C, both measured at standard atmospheric pressure. The Celsius scale is primarily used in most countries worldwide, especially in science, medicine, and daily weather reports.
Fahrenheit Scale (°F)
The Fahrenheit scale, created by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, is commonly used in the United States and some Caribbean countries. The scale is based on the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F. These two points are spread over a range of 180 degrees, unlike the 100-degree range in the Celsius scale. This results in a more precise representation of temperature changes, particularly in everyday weather conditions.
While the Celsius scale is more commonly used, especially in scientific contexts, the Fahrenheit scale remains relevant in certain regions and applications. Therefore, understanding how to convert between these two scales can be important for travelers, scientists, and anyone dealing with international temperature measurements.
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit: The Formula
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use a simple mathematical formula:
°F=(°C×95)+32°F = (°C \times \frac{9}{5}) + 32°F=(°C×59)+32In this formula:
- Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9.
- Divide the result by 5.
- Add 32 to the result.
Let’s apply this formula to convert 36.9°C to Fahrenheit.
Converting 36.9°C to Fahrenheit
To convert 36.9°C to Fahrenheit, we follow these steps:
- Multiply 36.9 by 9:
36.9×9=332.136.9 \times 9 = 332.136.9×9=332.1
- Divide the result by 5:
332.15=66.42\frac{332.1}{5} = 66.425332.1=66.42
- Add 32 to the result:
66.42+32=98.42°F66.42 + 32 = 98.42°F66.42+32=98.42°F
Thus, 36.9°C is equivalent to 98.42°F.
The Importance of 36.9°C in Medical Contexts
Now that we have converted 36.9°C to 98.42°F, it’s important to understand why this particular temperature is often significant, especially in medical contexts.
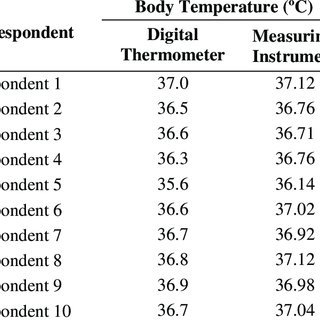
36.9°C, or 98.42°F, is very close to the normal human body temperature. In most cases, the average human body temperature is considered to be around 37°C (98.6°F). However, slight variations can occur due to several factors, including time of day, physical activity, and individual differences. A body temperature of 36.9°C is generally considered within the normal range, indicating that the person is healthy and not experiencing fever or hypothermia.
Fever and Temperature
A fever is generally defined as a body temperature higher than 38°C (100.4°F). When body temperature rises, it is often a sign that the body is fighting an infection. Monitoring body temperature is an essential part of diagnosing illnesses, and understanding temperature conversions can be crucial, especially in regions that use different temperature scales.
For instance, a doctor in the United States might interpret a temperature reading of 98.42°F (36.9°C) as normal, while someone unfamiliar with Fahrenheit might not immediately recognize this equivalence. Therefore, converting temperatures accurately is key to providing proper medical care and understanding one’s health status.
Historical Context and Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
Beyond the medical field, understanding temperature conversions has historical significance and practical applications in various industries.
The Origins of the Fahrenheit Scale
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit’s creation of the Fahrenheit scale was based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and the average human body temperature, which he initially placed at 96°F (later adjusted to 98.6°F). The Fahrenheit scale was widely adopted in the 18th century, particularly in English-speaking countries. Today, however, most of the world uses the Celsius scale, except for the United States and a few other regions.
Celsius and Its Scientific Significance
The Celsius scale gained prominence in scientific contexts because of its simplicity and alignment with the metric system, which is based on powers of ten. Scientists favor the Celsius scale for ease of calculation and its close relationship with the Kelvin scale, used in thermodynamics to measure absolute temperatures.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
Temperature conversion is essential in several industries, including:
- Meteorology: Weather reports are often given in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, depending on the region. For example, if you’re traveling to the United States from Europe, knowing how to convert temperatures helps you better understand the weather forecast.
- Cooking: Many international recipes list temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Being able to convert between these two units ensures that your cooking temperature is accurate, which can be critical for baking and other precise cooking methods.
- Science and Engineering: Many fields of science, such as chemistry and physics, use Celsius and Kelvin for temperature measurements. However, engineers working in regions that still use Fahrenheit need to be proficient in converting between scales to ensure accuracy in their calculations.
The Global Relevance of Temperature Conversion
As our world becomes more interconnected, understanding how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit becomes increasingly important. Whether you’re traveling, working in a field that involves temperature measurements, or simply trying to follow a recipe, being able to perform this conversion quickly and accurately is a valuable skill.
For instance, climate scientists studying global warming need to communicate findings to audiences worldwide. Since most of the world uses Celsius, but some regions use Fahrenheit, researchers often provide both measurements when discussing temperature changes. This ensures that the audience, regardless of location, can comprehend the data and its implications.
Conclusion
In summary, converting 36.9°C to Fahrenheit gives us a result of 98.42°F, a temperature close to the average human body temperature. Understanding how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is not just a matter of mathematical knowledge; it has practical applications in medicine, science, meteorology, cooking, and everyday life. The ability to interpret temperature readings across different scales can enhance our comprehension of the world, improve communication in international contexts, and, most importantly, help us maintain our health and well-being.
Temperature is more than just a number—it is a vital measure that influences decisions across various domains. Whether you’re tracking body temperature for medical reasons or following a weather report in another country, knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit ensures that you’re always informed.